Cryptonary’s thesis on Ethereum
Ethereum, the world’s second-largest crypto powerhouse behind Bitcoin, reigns as the top smart contract platform, sparking a financial revolution. In this report, we’re dishing out why you should ride the Ethereum wave, while weighing up reasons to hold off for balance—plus, our bold take on its future. Let’s dig in and uncover the full thesis...

Disclaimer: This is not financial or investment advice. You are responsible for any capital-related decisions you make, and only you are accountable for the results.
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a Layer-1 programmable blockchain that leverages smart contracts to enable a wide range of decentralised applications (dApps). To understand Ethereum, think of it as an operating system for the decentralised web, much like iOS or Android, which serve as the operating systems for smartphones, or Windows and MacOS, which function for computers. Just as these operating systems host applications like Facebook, Zoom, or Calculator, Ethereum hosts decentralised applications in the Web3 ecosystem.Consider this analogy: Bitcoin allows Alice to send money to Bob without needing a bank, serving as a decentralised form of currency.
But what if Alice wants to send $10 to Bob only if he completes a specific task by a future date? In that case, Alice can use Ethereum to create a smart contract—a self-executing contract with the terms directly written into code. The contract automatically sends the money to Bob upon verifying that he has completed the task.
This is just a simple example; Ethereum's true power lies in enabling the creation of much more complex workflows and decentralised applications, all driven by smart contracts. These smart contracts are the basis for decentralised finance (DeFi)—lending, exchanges, and all other DeFi activities.
The DeFi Summer was the Web3 equivalent of the Cambrian explosion. In a very short amount of time, thousands of dApps (decentralised applications) were launched on Ethereum. From exchanges like UNISwap to lending protocols like Aave, DeFi went from a concept to a reality.
Whereas Bitcoin is money, Ethereum (through smart contracts) provides a way to use blockchain beyond buying and holding crypto.
Who created Ethereum?
Ethereum was created by programmer Vitalik Buterin and launched in 2015. It is an open-source, decentralised blockchain platform that facilitates transactions, smart contracts, and decentralised applications. The Ethereum Foundation runs Ethereum as a type of decentralised organisation of contributors.What is ETH?
Ether (ETH) is the native token of Ethereum and the second-largest cryptocurrency in terms of market capitalisation after Bitcoin. Ethereum is the blockchain, and Ether (ETH) is the token used to facilitate transactions on the blockchain.The bullish case for Ethereum
Ethereum is the backbone of the Web3 economy, serving as the essential infrastructure that supports decentralised applications and smart contracts. Suppose Bitcoin is the foundation of the decentralised financial system. In that case, Ethereum is the framework—the pillars that hold up the entire ecosystem, enabling a new wave of innovation and functionality beyond just currency.ETH fuels this online economy; DeFi is the gold rush, and ETH is the shovel. This is why we think ETH should be your portfolio and one of our long-term bets on the future of crypto.
For people looking for a safer bet, lower down on the risk curve, Ethereum is the go-to because, after Bitcoin, it is the most active, popular, and liquid ecosystem. If Ethereum delivers on its promise, it has the potential to become the foundation for the future of finance.
Ethereum represents the first iteration of a new breed of blockchain—a programmable one. With its first-mover advantage, Ethereum has a dominant position in the quest to create a new financial system that is decentralised and without the interference and bureaucracy that define traditional finance.
Market opportunity
Given enough time, the market for Ethereum is essentially unquantifiable - global wealth is estimated at $454 trillion.
However, in the immediate term, Ethereum is spawning new markets, new wealth generation, and new sources of revenue. The global banking sector's net interest income alone was $8.5 trillion in 2023. RWAs (real-world assets) are a branch of Web3 that seeks to bring tangible, real-life assets on-chain—like ownership rights for houses, watches, stocks, and treasury bills.
7 out of 10 Institutional investors are interested in digital assets, and Ethereum has a depth to accommodate their interest. Fidelity Digital Assets conducted a survey in July 2021 which states:
- 71% of institutional investors plan to buy or invest in digital assets
- 90% of interest institutions expect to invest within the next five years
- 80% of institutional investors believe digital assets must be part of a portfolio
“The increased interest and adoption we’re seeing is a reflection of the growing sophistication and institutionalisation of the digital assets ecosystem.”
Ethereum will become the gateway for much of this capital. Ethereum is uniquely positioned to become the gateway for much of this capital because it has the largest DeFi ecosystem, TVL stats, and liquidity by some distance.
With a substantial addressable market in the hundreds of trillions of dollars, the upside potential for the ecosystem, as outlined above, and even if it only captures a small percentage of it, means there is still considerable growth potential.
Ethereum’s position right now as the face of Web3 is unlikely to change in the next 5-10 years, and so, for all intents and purposes, the growth of Web3 is the growth of Ethereum.
Ethereum has dominated because of its reliability. Where competitors like Solana have struggled to maintain 100% uptime, and Avalanche faces technical roadblocks and a lack of interest in its ecosystem, Ethereum remains the go-to for most sizeable DeFi operations.
Ethereum ETFs
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are investment vehicles that track the value of an asset (such as a stock or commodity). They allow investors to gain exposure to the underlying asset without directly owning it. These investment products trade on exchanges and can be accessed like traditional stocks through a brokerage account.Crypto ETFs operate on the same premise: They provide a way for investors to gain exposure to cryptocurrencies without the hassles of managing the coins themselves. This goes against the entire ethos of digital assets, but capitalism or institutional money is here to stay, and it is not pally with the term 'self-custody'.
Crypto ETFs will continue to be a massive on-ramp for retail participation in the crypto economy. As of March 2024, the value of assets managed by exchange-traded funds globally is over $9.5 trillion.
With the Ethereum spot ETF approved, capital will flow to the ecosystem indirectly. A spot ETF must be backed directly by ETH. For pension funds and larger players, they have another avenue other than Bitcoin to invest in crypto, allowing for diversification of their crypto allocations. This will inject fresh capital into the Ethereum ecosystem over the longer term.
Ethereum’s dominance
Ethereum’s dominance in all measurable performance statistics shows it has the deepest liquidity. Of the $96 billion locked in DeFi, Ethereum holds around $46 billion.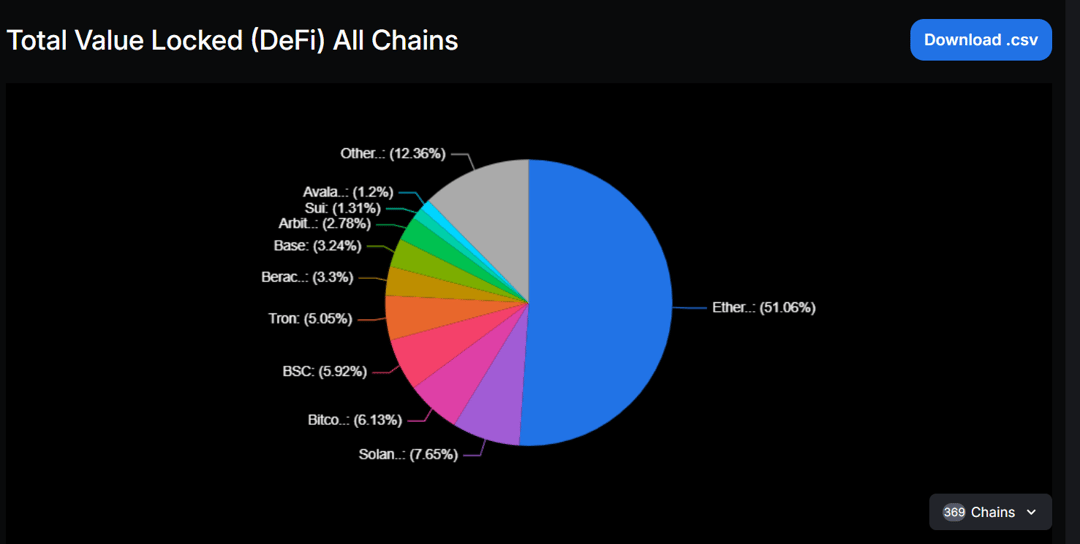
TVL, or Total Value Locked, measures the liquidity locked within a protocol or chain. This could come from assets locked:
- Users can swap with less slippage in a DEX (decentralised exchange). Slippage is a term used to describe the assets lost in a swap due to low liquidity.
- Ethereum, with the deepest liquidity pools (and the largest DEXs), is attractive for moving wealth around with minimal losses.
- In a lending protocol, the more assets available to borrow, the more interest is paid, and the more attractive it becomes for those with liquidity to add more, fueling an increase in the depth of the liquidity within the system.
- NFTs on Ethereum have become a bit of a status symbol within the crypto community. Examples include Bored Ape Yacht Club, a collection of NFTs that are highly sought after - primarily for clout. But they’re valuable nonetheless, with a floor price (the cheapest token in the collection you can buy) costing tens of thousands of dollars.
Additionally, Ethereum has a vast, well-established ecosystem. A key example of Ethereum’s success and desirability is that some of the largest wealth management funds, like BlackRock, chose Ethereum for their flagship crypto projects.
It enjoys this position as the first popular smart-contract capable chain. No matter what newer protocol launches, this cannot be taken away from Ethereum, which makes it unique. The length of time since launch is essentially a function of trust in the protocol. Huge stakeholders consider Ethereum their first choice protocol, bringing their capital to the ecosystem and facilitating the continuation of the snowball effect that defines Ethereum today - and into the future.
Let’s talk about Ethereum L2s
While Ethereum is a powerful platform, it faces challenges, particularly when it comes to scalability. This has led to the emergence of the so-called “Ethereum killers”—alternative protocols designed to address these limitations. However, instead of replacing Ethereum, another approach focuses on enhancing it through Layer 2 (L2) solutions. Let’s explore the scalability issues Ethereum faces and how L2 solutions aim to overcome them.L1 vs. L2
Layer 1 (L1) refers to the base layer or main blockchain, like Ethereum. Upgrades to L1, such as Ethereum’s shift from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake, are known as ‘on-chain’ scaling solutions. These upgrades typically require fundamental changes to the blockchain's core technology, often involving a hard fork to implement new consensus mechanisms or other key features.On the other hand, a Layer 2 (L2) solution is a secondary framework or protocol built on top of the existing L1 blockchain. The purpose of an L2 solution is to enhance the blockchain's scalability and throughput without modifying its underlying structure. This is known as ‘off-chain’ scaling.
L2 solutions create an additional layer where transactions and processes can occur independently from the main chain. The L1 layer continues to provide security and maintain the ledger's integrity, while the L2 layer enables a higher volume of transactions to be processed more efficiently.
There’s a long list of Layer-2 protocols within Ethereum; they are faster, cheaper, and less congested than Ethereum—all working together to make Etherum more scalable. Traffic between Ethereum and its Layer-2s adds another source of revenue for not just Ethereum but also its secondary protocols. Prominent Layer-2s include Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync.
The Scalability Trilemma
The Scalability Trilemma describes the complex relationship between three fundamental aspects of blockchain technology: decentralisation, scalability, and security. Each of these elements is essential to a blockchain's integrity and functionality, but achieving an optimal balance between them is challenging. The trilemma suggests that a blockchain can maximise two of these qualities, but often at the expense of the third.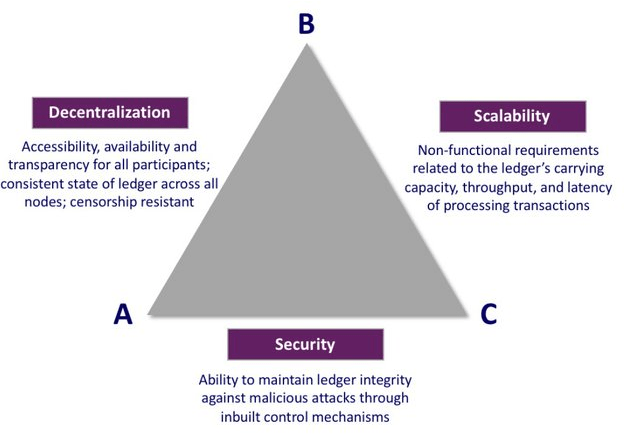
Let’s break down each side of the trilemma with examples:
- Decentralisation and security (but limited scalability): Bitcoin and Ethereum are prime examples of blockchains that prioritise decentralisation and security. Their robust, distributed networks and strong consensus mechanisms ensure they remain secure and resistant to censorship. However, this focus comes at the cost of scalability—both Bitcoin and Ethereum have faced issues with slower transaction speeds and higher fees as their networks grow.
- Security and scalability (but less decentralisation): Protocols like the XRP Ledger and Stellar are designed to be secure and scalable, enabling fast and cost-effective transactions. However, they achieve this by sacrificing some degree of decentralisation, often relying on a smaller set of validators or more centralised structures to maintain their efficiency.
- Decentralisation and scalability (but less security): NANO and VeChain emphasise decentralisation and scalability, allowing for rapid and widespread transactions. Yet, these blockchains may not offer the same level of security as more established networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum, making them more vulnerable to attacks.
For example, Ethereum’s recent Shanghai upgrade, which transitioned the network from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS), has enhanced its energy efficiency and security. However, Ethereum remains relatively slow and expensive compared to newer blockchains like Solana and Avalanche, designed to be more scalable but haven’t yet matched Ethereum's security and decentralisation.
Despite these challenges, Ethereum remains the preferred platform for decentralised finance (DeFi) and other applications, mainly due to its battle-tested infrastructure. While Solana has struggled with outages and Avalanche has yet to capture a significant market share, Ethereum’s flexibility and continuous upgrades—such as the introduction of new token standards like ERC-721, which powered the NFT market—have helped it maintain its dominance.
It’s important to remember that all chains are never complete. They are constantly going through upgrades, updates, and adding new utility. This reflexivity and flexible infrastructure have kept Ethereum relevant and held its would-be killers at bay.
Data highlights an impressive growth in the Layer 2 sector over the last years, with active addresses reaching upwards of 8.18 million, showcasing expansion as these solutions provide efficient transaction solutions and reduced gas fees. Particularly, platforms like Base and Arbitrum have seen substantial user activity and are leaders in the L2 race.
Most L2s are now cheaper and faster than alternative solutions like Avalanche or Solana. However, despite massive growth, L2s still remain a very fragile solution in terms of security. Most of the L2s are akin to centralised custodies due to weak security designs and centralisation.
However, we need to admit, the Ethereum ecosystem has scaled, L2 vision is playing out exactly as it was outlined in their roadmap, and users are enjoying cheap and fast transactions on L2s. But does that mean it's all smooth sailing? Not quite…
Ethereum's L1 stagnation
In contrast, Ethereum's main layer has not mirrored this expansive trend. With approximately 1.87 million active addresses, averaging around 400k users daily. It shows that while the main layer retains a substantial user base, it is not experiencing the growth seen in Layer 2 environments and is stagnating.This indicates that existing users are staying within the ecosystem, but it's unable to attract new users due to limited scalability, poor UX and high gas fees.
RWA and stablecoin dynamics
Interestingly, despite the stagnation in user growth on L1, it remains a predominant platform for Real World Assets (RWA) and stablecoins. The stablecoin market cap on Ethereum's L1 is significantly higher, sitting at around $120 million, compared to just $10 million on L2 platforms.This discrepancy points to a continued trust and preference for Ethereum's main layer when it comes to more substantial financial operations and RWA engagements, likely due to its established security and decentralized nature.
This contrast between user activity on L2s and real capital concentration on L1 highlights a key trend - while day-to-day transactions are moving to L2s, serious capital still trusts Ethereum's base layer.
The fact that RWAs, stablecoins, and institutional-grade assets remain heavily anchored on L1 underscores its role as the settlement layer for high-value operations. However, Ethereum Mainnet still faces a lot of challenges, and many users simply don't like using the Mainnet when there are better alternatives like Solana or L2s
The Pectra upgrade could be pivotal to solving this, making Ethereum's L1 more efficient without compromising the security that keeps major financial activity rooted there.
With the Pectra upgrade set to improve scalability, efficiency, and staking mechanics, Ethereum is positioned to solidify its lead and redefine how users interact with blockchain. Let's now dive into what the upgrade is all about!
The Pectra Upgrade
The Pectra upgrade is one of Ethereum's most significant developments to date, introducing key improvements in network efficiency, scalability, and user experience. A new testnet, Hooli, went live on March 17, 2025, with Pectra testing scheduled for March 26, 2025, to finalise preparations.If the Hooli test succeeds, the Mainnet upgrade is expected in late April or early May 2025, with developers finalising the exact date after assessing test results.
Rollout will be phased, and Pectra aims to streamline staking, enhance transaction flexibility and user experience, and lay the foundation for long-term scalability. Here is what is planned:
Phase 1: Immediate Enhancements
EIP-7251 - Increased Max Staking BalanceEIP-7251 increases Ethereum's maximum effective staking balance from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH per validator, significantly altering how staking is structured. Previously, staking more than 32 ETH required running multiple validator instances, leading to higher network overhead, increased signature processing, and operational inefficiencies.
By allowing larger stakes per validator, this upgrade reduces computational load, simplifies management, and enhances consensus efficiency.
For institutional validators and liquid staking providers, this change is good. Large-scale stakers can now consolidate thousands of validators into fewer instances, lowering gas fees, infrastructure costs, and signature processing demands per epoch.
Liquid staking protocols like Lido and Rocket Pool benefit from easier validator scaling, making reward distribution and staking operations more efficient. Along with this, the recent filings for Staked Ethereum ETFs and its potential approval in 2025 are bullish for ETH, and the upgrade is timely for institutional players.
However, this shift also introduces centralisation risks. Fewer validators controlling larger stakes could increase the influence of institutional entities, potentially reducing network decentralisation. While solo stakers remain unaffected, EIP-7251 optimises staking efficiency but comes with trade-offs, requiring ongoing monitoring to prevent excessive control by large entities.
EIP-7702 - Account Abstraction
This is one of our favourite changes about this upgrade as it aims to reduce user friction when interacting with Ethereum and drastically improve the UX. Here is how:
- Paying Gas with any ERC-20 Tokens: Allows users to pay gas fees with tokens like USDC instead of ETH. Users don't need to hold ETH specifically for gas, making Ethereum more accessible, especially for newcomers who might only hold stablecoins or other tokens when first making their transactions.
- Third-Party Fee Sponsorship: This mimics a subsidised experience, as users can interact with Ethereum without paying gas directly. For example, a gaming dApp might cover gas to onboard new players, enhancing user adoption. Remember people complaining about high gas fees? Now, it can be outsourced, keeping the UX frictionless.
- Bundled Transactions: Account abstraction allows multiple actions (e.g., approving a token and executing a swap) to be batched into a single transaction. It reduces the number of times a user pays gas, lowering the perceived cost of interacting with Ethereum. Solana and other non-EVM chains enjoy fewer clicks per user, which was the main argument for the bad experience on EVM land. Now, this will be changed.
EIP-6110 - On-chain validator deposit processing
EIP-6110 streamlines validator deposits by shifting their processing from the beacon chain to the execution layer, significantly reducing activation delays. Currently, validator deposits undergo a multi-step process where execution layer transactions must be manually included by beacon chain proposers, causing wait times of several hours before activation.
By integrating deposits directly into execution blocks, EIP-6110 eliminates dependency on consensus-layer polling, reducing activation time significantly. This upgrade not only enhances Ethereum's staking infrastructure but also makes the validator onboarding process more predictable and efficient.
Faster activation ensures better network responsiveness, benefiting solo stakers, institutional validators, and liquid staking providers alike. While EIP-7702 was about improving the UX of users, EIP-6110 improves the UX of validators.
Phase 2: Long-term scalability & efficiency
In the second phase of the Pectra upgrade, Ethereum introduces critical enhancements that focus on long-term scalability and network efficiency, which are essential for maintaining Ethereum's competitiveness in the blockchain space. Warning, very technical…PeerDAS (Peer Data Availability Sampling):
- PeerDAS is designed to enhance data availability and reliability, a fundamental aspect for the successful operation of Layer-2 rollups. This upgrade is a preparatory step towards more comprehensive sharding solutions expected in future Ethereum updates.
- By improving data handling capabilities, PeerDAS ensures that information is more accessible and verifiable across the network, which is crucial for maintaining high security and functionality as the network scales.
- Replacing the older Merkle Patricia Trees (primarily used to store the blockchain's state, transaction data, and receipts) with Verkle Trees, this update significantly reduces the state size on the Ethereum blockchain.
- The reduction in state size facilitates faster transaction verification and also aids in the transition towards stateless clients. This shift is expected to lower the hardware requirements for validators, potentially increasing network decentralisation by allowing more participants to run nodes.
Why the Pectra upgrade matters
The Pectra upgrade is a major step forward for Ethereum, bringing improvements in scalability, security, and user experience. It's designed to enhance Ethereum's core infrastructure for the long-term evolution of the network. From validator upgrades to better transaction handling, these changes make Ethereum more efficient, accessible, and future-ready.Scalability & security: Strengthening Ethereum's foundation
By increasing validator flexibility and introducing account abstraction, Ethereum is streamlining its operations to make staking easier and transactions more flexible. These improvements make Ethereum more attractive to institutional players and enterprise adoption. As demand for blockchain infrastructure grows, Ethereum's ability to scale efficiently will be key to maintaining its dominance.A More Developer-Friendly Ecosystem
Ethereum is making it easier than ever to build on the network. With programmable externally owned accounts, improved cryptographic efficiency, and higher data throughput, developers can create more complex and efficient applications without friction. Whether it's DeFi, gaming, or tokenised assets, Ethereum's more versatile development environment is set to attract a broader range of builders.A thriving developer ecosystem leads to new applications, more innovation, and increased adoption-all of which add to Ethereum's long-term value.
Better UX = Higher adoption
For everyday users, Pectra makes interacting with Ethereum simpler and more flexible. Features like paying gas fees in tokens other than ETH or automating transactions improve accessibility, removing one of the biggest pain points for newcomers. A smoother, more user-friendly experience encourages more people to engage with Ethereum, boosting network activity and security.The UX has been the pain point of the Ethereum mainnet and the broader EVM ecosystem for years. This upgrade can be a game changer in terms of bringing more user friendly blockchain experience and increasing adoption.
Future-Proofing Ethereum: Preparing for What's Next
Blockchain adoption is growing, countries and institutions have never been more bullish on blockchain technology, and Ethereum needs to stay ahead of rising demand. Pectra's focus on scalability, transaction efficiency, and validator optimisation ensures that the network can handle more users, more applications, and larger-scale operations without performance trade-offs.With technical advancements aligning with potential regulatory tailwinds, Ethereum is setting itself up for sustained growth and broader adoption. However, price hasn't been catching up with the latest developments, let's examine the price action and valuation more closely.
Valuation exercise + price targets
Ethereum provides the foundation for building a viable decentralised financial system, and that’s why we believe it can eventually overtake Bitcoin. Bitcoin, as of today, is a non-productive asset; it is a store of value comparable to gold in its function. Ethereum, however, provides the means to rebuild the financial infrastructure and almost every other part of the global on-chain via smart contracts.Ethereum might not stay as dominant as it is, which is highly unlikely. But given the numbers we’re talking about in the sections above, it is still the top dog, second only to Bitcoin.
For Ethereum's valuation, we employed a mix of quantitative and qualitative methods. First, we analysed Ethereum's historical fully diluted market by regressing it with time as an independent variable.
As a result, we developed a model (blue linear line) that explains 52% of Ethereum's market cap variance. We extended the model to estimate Ethereum's future market cap.
The blue line is the best-fit model, resulting in a linear line with minimum error (residuals). Even though the blue model has relatively high accuracy, crypto has seasonality and experiences bull and bear markets where prices are far from linear. As a result, there are some residuals from the model.
To further minimise them, we calculated the standard deviation of errors. That results in a range where the most errors occur. We added and subtracted one standard deviation of residuals from our blue model, resulting in the upper and lower bounds of the model. Further, to determine the price of Ether, we assumed a static supply of ETH. Ethereum's tokenomics are interesting because it can be both inflationary and deflationary. Historically, it has approximately the same supply with negligible differences below 0.01%.
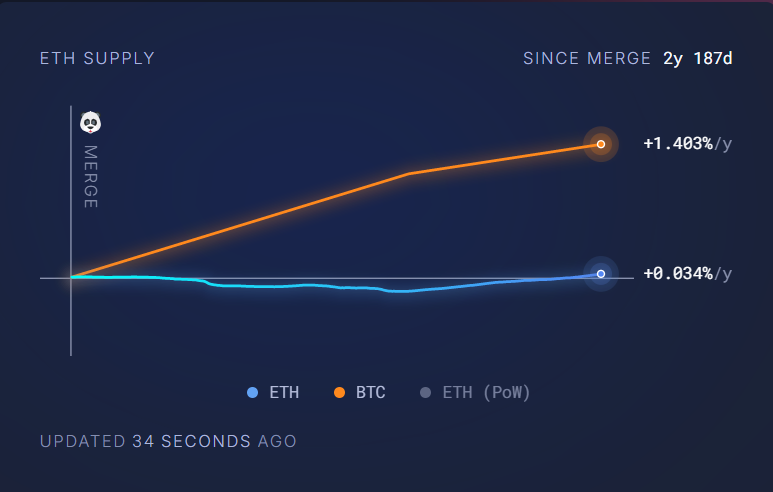
Therefore, it makes sense to consider it somewhat static. As a result of our analysis, we came up with the following scenarios for short-term and long-term:
For the 24/25 cycle
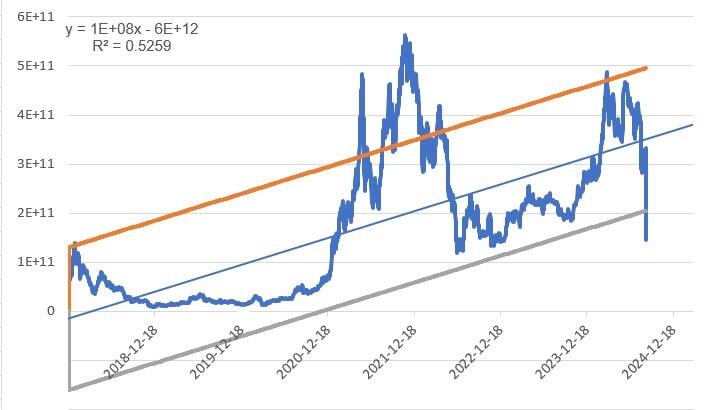
Base case scenario: this is our model's lower bound (grey line). Based on this bearish scenario, our model estimates Ethereum's fully diluted market cap to be $280b in the 24/25 cycle.
Bull case scenario: This is our model's main trend (blue line). Based on this scenario, our model estimates Ethereum's fully diluted market cap to be $424b in the 24/25 cycle.
Best-case scenario: This is our model's upper bound (orange line). Based on this scenario, our model estimates Ethereum's fully diluted market cap to be $570b in the 24/25 cycle.
For the longer term (2032)
We have stopped using an arbitrary 2030 for our longer-term targets and adopted two Bitcoin cycles from the current cycle. This places our long-term timeframe in 2032. Therefore, we employed the same methodology as in our short-term estimations and extended the model until 2032 to estimate the future value of Ethereum’s market cap.As a result, the model came up with the following scenarios for 2032.
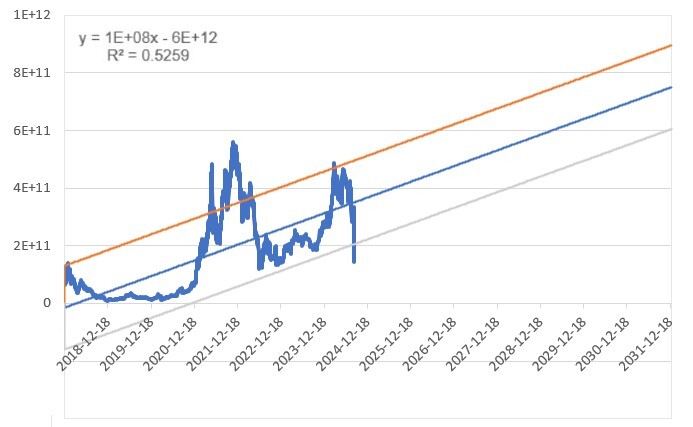
Base case scenario: this is our model's lower bound (grey line). Based on this scenario, we can expect the market cap of Ethereum to be roughly $907b by 2032
Bull case scenario: This is our model's middle line (blue line). Based on this scenario, Ethereum's market cap will be roughly $1.1t by 2032.
Best-case scenario: This is our model's upper bound (orange line). Based on this scenario, Ethereum's market cap will be roughly $1.34t by 2032.
Here is the summary table of our estimates plus the potential price of Ethereum.
Model estimates for 2032
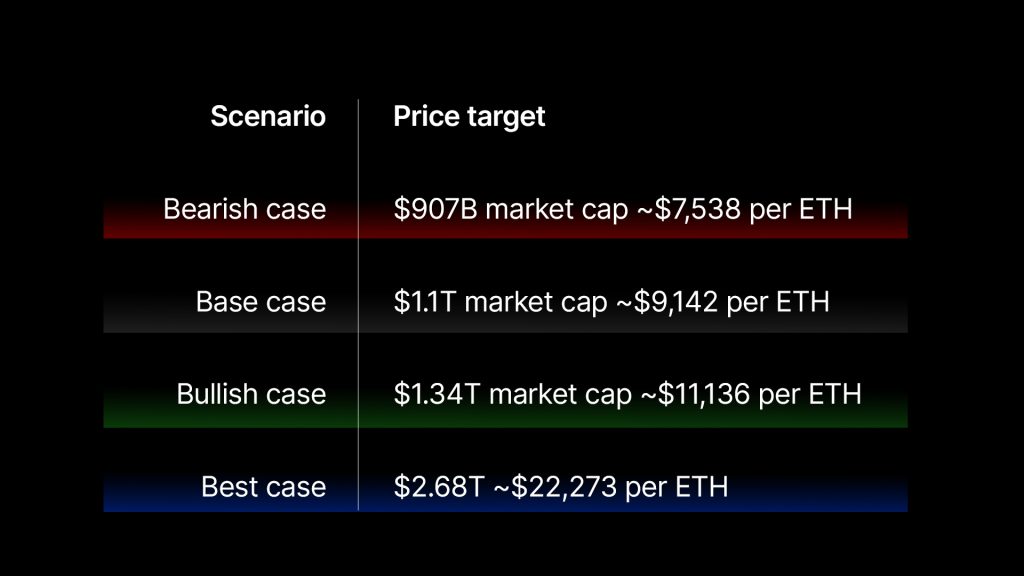
Cryptonary’s definitive ETH price targets
24/25 price targets- Base case: ~$4,240 | 1.93x upside
- Bullish case: ~$5,700 |2.59x upside
- Best case: ~$11,400 |5.18x upside
- ~$22,273 |10.13x upside
How to buy ETH
Dollar-cost averaging (buying equal amounts every day/week/month) in ETH has been a proven strategy for minimising the impact of volatility over time.Buying on a centralised exchange
Step 1: Choose a centralised exchangePopular exchanges for buying Ethereum include Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, and Gemini. Select a reputable exchange that operates in your country and offers competitive fees.
Step 2: Create and verify your account
- Sign up for an account using your email address and create a strong password.
- Complete the identity verification process by uploading a photo ID and providing additional information as the exchange requires.
- Deposit fiat currency (USD, EUR, etc.) into your account via bank transfer, credit/debit card, or other supported payment methods.
- Ensure your account is funded before attempting to buy ETH.
- Go to the trading section of the exchange and find the ETH trading pair that matches your deposited currency (e.g., ETH/USD, ETH/EUR).
- Choose between a market or limit order:
- Market order: Buy ETH at the current market price.
- Limit order: Specify the price at which you want to buy ETH. The order will execute when the market price matches your limit price.
- Enter the amount of ETH you want to purchase and confirm the order.
- After buying ETH, transferring it to a secure wallet is recommended.
- Withdraw ETH from the exchange to your personal Ethereum wallet address for safekeeping.
Buying Ethereum using a wallet app
Step 1: Choose a walletSelect a secure Ethereum wallet. Options include:
- Mobile wallets: Trust Wallet, MetaMask, or Exodus.
- Hardware wallets: Ledger or Trezor.
Step 2: Set up your wallet
- Create a new wallet and securely back up the recovery phrase provided.
- Follow the setup instructions and enable security features such as two-factor authentication if available.
Some wallets, like Trust Wallet and MetaMask, have integrated features to buy Ethereum directly.
- You can purchase ETH using the “Buy” option within the wallet app, as well as a debit card, bank transfer, or other supported payment methods.
- Alternatively, you can transfer ETH from a centralised exchange to your wallet address.
- If buying directly through the wallet, choose ETH, enter your purchase amount, and select your payment method.
- Follow the prompts to complete the purchase. The ETH will be deposited into your wallet once the transaction is processed.
- After the transaction is complete, check your wallet balance to ensure the ETH has arrived.
Via Phantom Wallet
You can now purchase Ethereum (ETH) directly using the Phantom wallet.- Open Phantom: Launch the Phantom application on your device.
- Initiate purchase: Click the "Buy" button on the main interface.
- Select Ethereum: Choose the Ethereum token from the list of available cryptocurrencies.
- Specify amount: Enter the amount of Ethereum you wish to purchase.
- Choose a provider: You can select a purchase provider from Coinbase Pay, Transak, Blockchain.com or enter card details.
- Complete the purchase: A pop-up window will appear for your selected provider; fill in the necessary information to complete the transaction.
Invalidation criteria
Our bullish thesis on Ethereum is grounded in its established dominance, robust ecosystem, and potential for future growth. However, several short-term and long-term risks could invalidate this outlook. Monitoring these potential threats is essential to maintain an accurate and up-to-date investment thesis.Short-term invalidation criteria:
- Significant security breach: If Ethereum experiences a major hack or security vulnerability that compromises the integrity of the network or results in substantial loss of funds, it could severely damage trust in the platform and lead to a significant decline in usage and value.
- DeFi Collapse: A systemic failure in the DeFi ecosystem built on Ethereum, possibly due to a major protocol hack or market crash, could severely impact Ethereum's utility and value proposition. Such an event would undermine the trust and participation in DeFi, one of Ethereum's primary use cases.
- Regulatory crackdown: Severe regulatory actions against Ethereum or the broader cryptocurrency market in major economies, particularly the United States or European Union, could significantly impact adoption and use. Restrictive regulations could limit the ability of institutions and individuals to engage with the Ethereum network, stifling its growth.
- Technological obsolescence: If a competing blockchain emerges that demonstrably solves the scalability trilemma—achieving superior decentralisation, security, and scalability—and rapidly gains market share at Ethereum's expense, Ethereum's position as the leading smart contract platform could be jeopardised.
- Loss of developer mindshare: Ethereum could gradually lose its competitive edge if it fails to maintain its dominant position in terms of active developers and the decentralised application (dApp) ecosystem. A decline in innovation and development activity would make it harder for Ethereum to adapt to future challenges and maintain its leadership.
- Quantum computing threat: The emergence of practical quantum computing could potentially break Ethereum's cryptographic security if adequate countermeasures are not implemented in time. This threat could undermine the fundamental security of the blockchain, leading to a catastrophic loss of trust.
- Macroeconomic Factors: A prolonged global economic recession or depression could severely impact risk assets, including cryptocurrencies. This economic downturn could stifle investment and adoption, potentially slowing Ethereum's growth and integration into the global financial system.
Cryptonary’s take
Ethereum remains the safest bet in the crypto space after Bitcoin, offering a well-established and robust platform that has proven its resilience and utility over time. It's highly unlikely that Ethereum will fade into irrelevance or be exposed as a scam, making it a reliable choice for long-term investors. For those interested in DeFi, Ethereum's ecosystem provides one of the most secure and established environments underpinned by the largest developer community and the deepest liquidity pools.However, Ethereum may not deliver the kind of explosive returns seen in the early days of crypto investing. Think of ETH as a bet on a tech giant like Apple or Tesla—solid and relatively safe, but not likely to turn a small investment into generational wealth. Instead, it offers steady growth potential with a strong foundation, making it a cornerstone in any diversified crypto portfolio.
While the potential for exponential gains may be lower compared to riskier altcoins, Ethereum's proven track record, ongoing development, and institutional backing make it a compelling long-term investment in the future of decentralised finance and Web3.
Content ledger
Layer 2 Digest: Why Ethereum's next upgrade mattersEthereum Digest: Deflation, surging stakes, and bears
Revealed: The best place to stake ETH
Ethereum: smaller supply, bigger demand - what this means for you









